子图作为 CompiledGraph
在 Spring AI Alibaba 中,可以先编译 StateGraph 得到 CompiledGraph,然后在其他 Graph 中复用,这种方式性能更好且更灵活。
CompiledGraph vs StateGraph
| 特性 | StateGraph | CompiledGraph |
|---|---|---|
| 定义时机 | 构建时 | 编译后 |
| 性能 | 需要每次编译 | 预编译,性能更好 |
| 灵活性 | 可修改 | 不可修改 |
| 复用 | 可以但需重新编译 | 直接复用 |
基本用法
创建并编译子图
创建并编译子图查看完整代码
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.CompiledGraph;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.KeyStrategy;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.KeyStrategyFactory;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.StateGraph;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.exception.GraphStateException;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.state.strategy.ReplaceStrategy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import static com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.StateGraph.END;
import static com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.StateGraph.START;
import static com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.action.AsyncNodeAction.node_async;
/**
* 创建并编译子图
*/
public static CompiledGraph createAndCompileSubGraph() throws GraphStateException {
KeyStrategyFactory subKeyFactory = () -> {
HashMap<String, KeyStrategy> strategies = new HashMap<>();
strategies.put("input", new ReplaceStrategy());
strategies.put("output", new ReplaceStrategy());
return strategies;
};
// 定义并编译子图
StateGraph subGraphDef = new StateGraph(subKeyFactory)
.addNode("process", node_async(state -> {
String input = (String) state.value("input").orElse("");
String output = "Processed: " + input.toUpperCase();
return Map.of("output", output);
}))
.addEdge(START, "process")
.addEdge("process", END);
// 编译子图
return subGraphDef.compile();
}
在节点中使用 CompiledGraph
在节点中使用 CompiledGraph查看完整代码
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.CompiledGraph;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.OverAllState;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.RunnableConfig;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.action.NodeAction;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 在节点中使用 CompiledGraph
*/
public static class CompiledSubGraphNode implements NodeAction {
private final CompiledGraph compiledGraph;
public CompiledSubGraphNode(CompiledGraph compiledGraph) {
this.compiledGraph = compiledGraph;
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> apply(OverAllState state) {
// 从父状态提取输入
String input = (String) state.value("data").orElse("");
// 执行编译好的子图
Map<String, Object> subInput = Map.of("input", input);
OverAllState subResult = compiledGraph.invoke(subInput, RunnableConfig.builder().build()).orElseThrow();
// 提取子图输出
String output = (String) subResult.value("output").orElse("");
return Map.of("result", output);
}
}
在父图中使用
在父图中使用查看完整代码
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.CompiledGraph;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.StateGraph;
import static com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.StateGraph.END;
import static com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.StateGraph.START;
import static com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.action.AsyncNodeAction.node_async;
/**
* 在父图中使用
*/
public static CompiledGraph useInParentGraph(CompiledGraph compiledSubGraph) throws GraphStateException {
KeyStrategyFactory parentKeyFactory = () -> {
HashMap<String, KeyStrategy> strategies = new HashMap<>();
strategies.put("data", new ReplaceStrategy());
strategies.put("result", new ReplaceStrategy());
return strategies;
};
StateGraph parentGraph = new StateGraph(parentKeyFactory)
.addNode("prepare", node_async(state ->
Map.of("data", "hello world")))
.addNode("subgraph", compiledSubGraph)
.addNode("finalize", node_async(state -> {
String result = (String) state.value("result").orElse("");
return Map.of("final", "Done: " + result);
}))
.addEdge(START, "prepare")
.addEdge("prepare", "subgraph")
.addEdge("subgraph", "finalize")
.addEdge("finalize", END);
return parentGraph.compile();
}
多个子图复用
同一个 CompiledGraph 可以在多个地方复用:
多个子图复用查看完整代码
/**
* 多个子图复用
*/
public static CompiledGraph reuseMultipleSubGraphs(CompiledGraph dataProcessor) throws GraphStateException {
KeyStrategyFactory keyFactory = () -> {
HashMap<String, KeyStrategy> strategies = new HashMap<>();
strategies.put("data", new ReplaceStrategy());
strategies.put("result", new ReplaceStrategy());
return strategies;
};
// 在多个节点中复用
StateGraph mainGraph = new StateGraph(keyFactory)
.addNode("process1", dataProcessor)
.addNode("process2", dataProcessor)
.addNode("process3", dataProcessor)
.addEdge(START, "process1")
.addEdge("process1", "process2")
.addEdge("process2", "process3")
.addEdge("process3", END);
return mainGraph.compile();
}
// 在多个节点中复用
StateGraph mainGraph = new StateGraph(keyFactory)
.addNode("process1", nodeasync(new CompiledSubGraphNode(dataProcessor)))
.addNode("process2", nodeasync(new CompiledSubGraphNode(dataProcessor)))
.addNode("process3", nodeasync(new CompiledSubGraphNode(dataProcessor)))
.addEdge(StateGraph.START, "process1")
.addEdge("process1", "process2")
.addEdge("process2", "process3")
.addEdge("process3", StateGraph.END);
带配置的子图
可配置的 CompiledGraph 包装器
可配置的 CompiledGraph 包装器查看完整代码
public class ConfigurableCompiledSubGraph implements NodeAction {
private final CompiledGraph compiledGraph;
private final Map<String, String> inputMapping;
private final Map<String, String> outputMapping;
public ConfigurableCompiledSubGraph(
CompiledGraph compiledGraph,
Map<String, String> inputMapping, // parentKey -> subKey
Map<String, String> outputMapping // subKey -> parentKey
) {
this.compiledGraph = compiledGraph;
this.inputMapping = inputMapping;
this.outputMapping = outputMapping;
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> apply(OverAllState parentState) {
// 映射输入
Map<String, Object> subInput = new HashMap<>();
inputMapping.forEach((parentKey, subKey) -> {
parentState.value(parentKey).ifPresent(value ->
subInput.put(subKey, value));
});
// 执行子图
OverAllState subResult = compiledGraph.invoke(subInput);
// 映射输出
Map<String, Object> parentOutput = new HashMap<>();
outputMapping.forEach((subKey, parentKey) -> {
subResult.value(subKey).ifPresent(value ->
parentOutput.put(parentKey, value));
});
return parentOutput;
}
}
// 使用
CompiledGraph processor = createProcessorGraph().compile();
NodeAction node1 = new ConfigurableCompiledSubGraph(
processor,
Map.of("userInput", "input"), // userInput -> input
Map.of("output", "processedData") // output -> processedData
);
NodeAction node2 = new ConfigurableCompiledSubGraph(
processor,
Map.of("rawData", "input"), // rawData -> input
Map.of("output", "cleanedData") // output -> cleanedData
);
并行执行多个 CompiledGraph
并行执行多个 CompiledGraph查看完整代码
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.List;
public class ParallelCompiledGraphNode implements NodeAction {
private final List<CompiledGraph> graphs;
public ParallelCompiledGraphNode(List<CompiledGraph> graphs) {
this.graphs = graphs;
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> apply(OverAllState state) {
String input = (String) state.value("input").orElse("");
// 并行执行所有子图
List<CompletableFuture<OverAllState>> futures = graphs.stream()
.map(graph -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
graph.invoke(Map.of("input", input))))
.toList();
// 等待所有完成
List<OverAllState> results = futures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.toList();
// 合并结果
List<String> outputs = results.stream()
.map(r -> (String) r.value("output").orElse(""))
.toList();
return Map.of("results", outputs);
}
}
// 使用
CompiledGraph graph1 = createGraph1().compile();
CompiledGraph graph2 = createGraph2().compile();
CompiledGraph graph3 = createGraph3().compile();
NodeAction parallelNode = new ParallelCompiledGraphNode(
List.of(graph1, graph2, graph3)
);
带 Checkpoint 的子图
CompiledGraph 可以有自己独立的 checkpoint:
带 Checkpoint 的子图查看完整代码
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.checkpoint.MemorySaver;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.CompileConfig;
// 子图使用独立的 checkpoint
var subCheckpointer = new MemorySaver();
var subCompileConfig = CompileConfig.builder()
.checkpointSaver(subCheckpointer)
.build();
CompiledGraph compiledSubGraph = subGraphDef.compile(subCompileConfig);
// 执行时指定子图的 threadId
public class CheckpointedSubGraphNode implements NodeAction {
private final CompiledGraph compiledGraph;
private final String subThreadIdPrefix;
public CheckpointedSubGraphNode(
CompiledGraph compiledGraph,
String subThreadIdPrefix
) {
this.compiledGraph = compiledGraph;
this.subThreadIdPrefix = subThreadIdPrefix;
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> apply(OverAllState state) {
String input = (String) state.value("input").orElse("");
// 为子图创建独立的运行配置
var subConfig = RunnableConfig.builder()
.threadId(subThreadIdPrefix + "-" + System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
// 执行子图
OverAllState result = compiledGraph.invoke(
Map.of("input", input),
subConfig
);
return Map.of("output", result.value("output").orElse(""));
}
}
�性能优化
预编译策略
预编译策略查看完整代码
// 服务启动时预编译所有子图
@Configuration
public class GraphConfiguration {
@Bean
public CompiledGraph validationGraph() {
StateGraph def = createValidationGraph();
return def.compile(); // 启动时编译一次
}
@Bean
public CompiledGraph transformGraph() {
StateGraph def = createTransformGraph();
return def.compile();
}
@Bean
public CompiledGraph aggregationGraph() {
StateGraph def = createAggregationGraph();
return def.compile();
}
}
// 在运行时直接使用预编译的图
@Service
public class WorkflowService {
@Autowired
private CompiledGraph validationGraph;
@Autowired
private CompiledGraph transformGraph;
@Autowired
private CompiledGraph aggregationGraph;
public void processData(String data) {
// 直接使用,无需重新编译
var result1 = validationGraph.invoke(Map.of("input", data));
var result2 = transformGraph.invoke(Map.of("input", data));
var result3 = aggregationGraph.invoke(Map.of("input", data));
}
}
完整示例
完整示例查看完整代码
// 1. 定义数据验证子图
public CompiledGraph createValidationGraph() {
KeyStrategyFactory keyFactory = () -> {
HashMap<String, KeyStrategy> strategies = new HashMap<>();
strategies.put("data", new ReplaceStrategy());
strategies.put("isValid", new ReplaceStrategy());
return strategies;
};
StateGraph graph = new StateGraph(keyFactory)
.addNode("validate", nodeasync(state -> {
String data = (String) state.value("data").orElse("");
boolean valid = data != null && !data.isEmpty();
return Map.of("isValid", valid);
}))
.addEdge(StateGraph.START, "validate")
.addEdge("validate", StateGraph.END);
return graph.compile();
}
// 2. 定义数据转换子图
public CompiledGraph createTransformGraph() {
KeyStrategyFactory keyFactory = () -> {
HashMap<String, KeyStrategy> strategies = new HashMap<>();
strategies.put("data", new ReplaceStrategy());
strategies.put("transformed", new ReplaceStrategy());
return strategies;
};
StateGraph graph = new StateGraph(keyFactory)
.addNode("transform", nodeasync(state -> {
String data = (String) state.value("data").orElse("");
return Map.of("transformed", data.toUpperCase());
}))
.addEdge(StateGraph.START, "transform")
.addEdge("transform", StateGraph.END);
return graph.compile();
}
// 3. 组合使用
CompiledGraph validationGraph = createValidationGraph();
CompiledGraph transformGraph = createTransformGraph();
StateGraph mainGraph = new StateGraph(keyFactory)
.addNode("validate", nodeasync(state -> {
String data = (String) state.value("input").orElse("");
OverAllState result = validationGraph.invoke(Map.of("data", data));
return Map.of("isValid", result.value("isValid").orElse(false));
}))
.addNode("transform", nodeasync(state -> {
String data = (String) state.value("input").orElse("");
OverAllState result = transformGraph.invoke(Map.of("data", data));
return Map.of("output", result.value("transformed").orElse(""));
}))
.addEdge(StateGraph.START, "validate")
.addConditionalEdges("validate",
edgeasync(state -> {
Boolean valid = (Boolean) state.value("isValid").orElse(false);
return valid ? "continue" : "error";
}),
Map.of("continue", "transform", "error", StateGraph.END))
.addEdge("transform", StateGraph.END);
CompiledGraph main = mainGraph.compile();
// 执行
OverAllState result = main.invoke(Map.of("input", "test data"));
System.out.println("Output: " + result.value("output").orElse(""));
附图
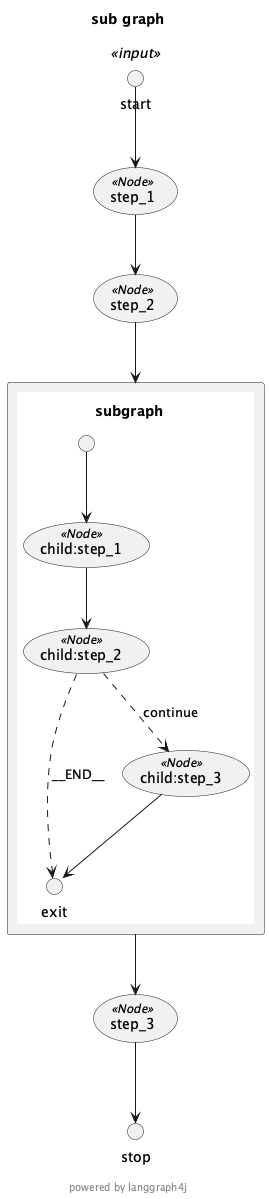
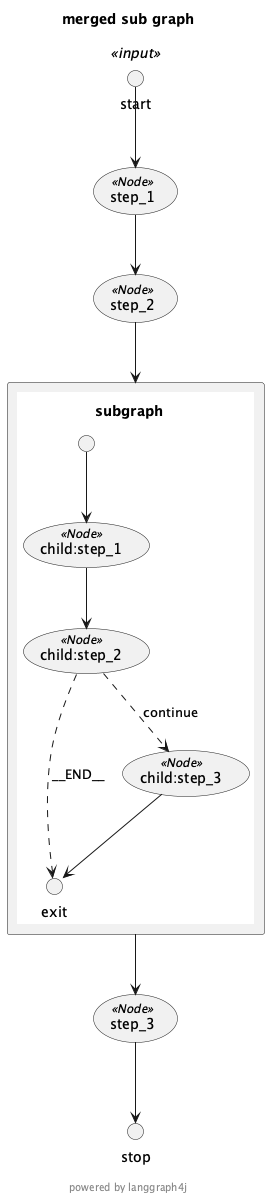
相关文档
- 子图作为 NodeAction - 节点包装方式
- 子图作为 StateGraph - 直接嵌入方式
- 快速入门 - Graph 基础使用