ETL 管道
提取、转换和加载 (ETL) 框架作为检索增强生成 (RAG) 用例中数据处理的支柱。
ETL 管道编排从原始数据源到结构化向量存储的流程,确保数据以 AI 模型检索的最佳格式存在。
RAG 用例通过从数据体中检索相关信息来增强生成模型的能力,从而提高生成输出的质量和相关性。
API 概述
ETL 管道创建、转换和存储Document实例。
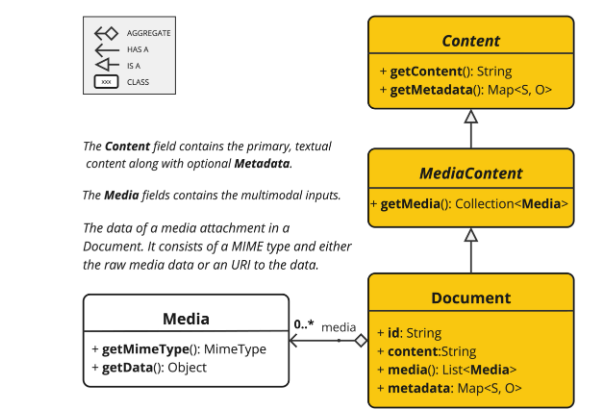
Document类包含文本、元数据以及可选的额外媒体类型,如图像、音频和视频。
ETL 管道有三个主要组件:
-
DocumentReader- 实现Supplier<List<Document>> -
DocumentTransformer- 实现Function<List<Document>, List<Document>> -
DocumentWriter- 实现Consumer<List<Document>>
Document类的内容是通过DocumentReader的帮助从 PDF、文本文件和其他文档类型创建的。
要构建一个简单的 ETL 管道,您可以将这三种类型的实例链接在一起。
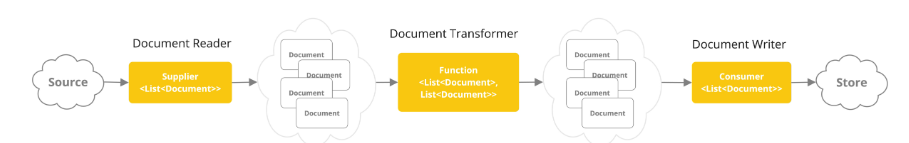
假设我们有以下 ETL 类型的实例:
-
PagePdfDocumentReader-DocumentReader的实现 -
TokenTextSplitter-DocumentTransformer的实现 -
VectorStore-DocumentWriter的实现
要执行将数据加载到向量数据库的基本操作以用于检索增强生成模式,请使用以下 Java 函数式语法代码:
vectorStore.accept(tokenTextSplitter.apply(pdfReader.get()));
或者,您可以使用更自然地表达领域的方法名:
vectorStore.write(tokenTextSplitter.split(pdfReader.read()));
ETL 接口
ETL 管道由以下接口和实现组成。 详细的 ETL 类图在 ETL 类图部分中显示。
DocumentReader
提供来自不同来源的文档源。
public interface DocumentReader extends Supplier<List<Document>> {
default List<Document> read() {
return get();
}
}
DocumentTransformer
转换一批文档作为处理工作流的一部分。
public interface DocumentTransformer extends Function<List<Document>, List<Document>> {
default List<Document> transform(List<Document> transform) {
return apply(transform);
}
}
DocumentWriter
管理 ETL 过程的最后阶段,准备文档进行存储。
public interface DocumentWriter extends Consumer<List<Document>> {
default void write(List<Document> documents) {
accept(documents);
}
}
ETL 类图
以下类图说明了 ETL 接口和实现。
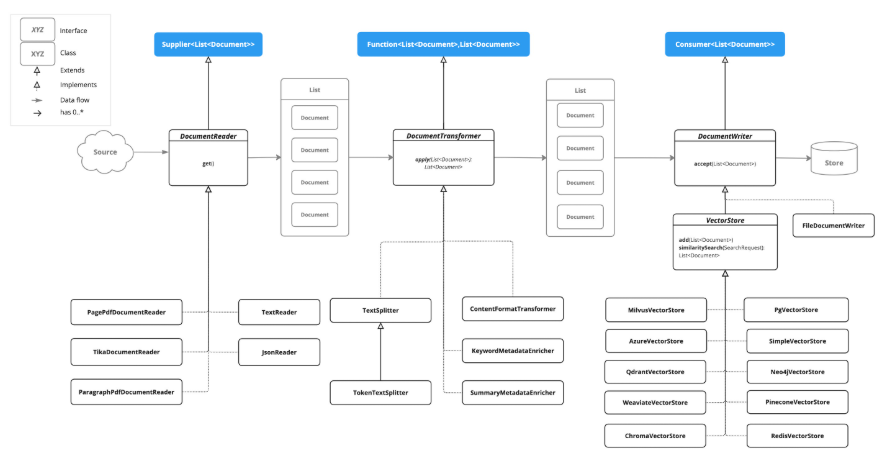
DocumentReaders
JSON
JsonReader处理 JSON 文档,将它们转换为Document对象列表。
示例
@Component
class MyJsonReader {
private final Resource resource;
MyJsonReader(@Value("classpath:bikes.json") Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
List<Document> loadJsonAsDocuments() {
JsonReader jsonReader = new JsonReader(this.resource, "description", "content");
return jsonReader.get();
}
}
构造函数选项
JsonReader提供了几个构造函数选项:
-
JsonReader(Resource resource) -
JsonReader(Resource resource, String… jsonKeysToUse) -
JsonReader(Resource resource, JsonMetadataGenerator jsonMetadataGenerator, String… jsonKeysToUse)
参数
resource: 指向 JSON 文件的 Spring Resource对象。
jsonKeysToUse: 从 JSON 中应该用作结果Document对象中文本内容的键数组。
jsonMetadataGenerator: 用于为每个Document创建元数据的可选JsonMetadataGenerator。
行为
JsonReader按以下方式处理 JSON 内容:
-
它可以处理 JSON 数组和单个 JSON 对象。
-
对于每个 JSON 对象(在数组中或单个对象中):
-
它根据指定的
jsonKeysToUse提取内容。 -
如果未指定键,则使用整个 JSON 对象作为内容。
-
它使用提供的
JsonMetadataGenerator(如果未提供则使用空生成器)生成元数据。 -
它创建一个包含提取内容和元数据的
Document对象。
-
使用 JSON 指针
JsonReader现在支持使用 JSON 指针检索 JSON 文档的特定部分。此功能允许您轻松地从复杂的 JSON 结构中提取嵌套数据。
get(String pointer)方法
public List<Document> get(String pointer)
此方法允许您使用 JSON 指针检索 JSON 文档的特定部分。
参数
pointer: 用于在 JSON 结构中定位所需元素的 JSON 指针字符串(如 RFC 6901 中定义)。
返回值
返回一个List<Document>,包含从指针定位的 JSON 元素解析出的文档。
行为
-
该方法使用提供的 JSON 指针导航到 JSON 结构中的特定位置。
-
如果指针有效并指向现有元素:
-
对于 JSON 对象:返回包含单个 Document 的列表。
-
对于 JSON 数组:返回 Document 列表,数组中的每个元素一个。
-
-
如果指针无效或指向不存在的元素,则抛出
IllegalArgumentException。
示例
JsonReader jsonReader = new JsonReader(resource, "description");
List<Document> documents = this.jsonReader.get("/store/books/0");
示例 JSON 结构
[
{
"id": 1,
"brand": "Trek",
"description": "A high-performance mountain bike for trail riding."
},
{
"id": 2,
"brand": "Cannondale",
"description": "An aerodynamic road bike for racing enthusiasts."
}
]
在此示例中,如果JsonReader配置为使用"description"作为jsonKeysToUse,它将创建Document对象,其中内容是数组中每辆自行车的description字段的值。
注意事项
-
JsonReader使用 Jackson 进行 JSON 解析。 -
它可以通过使用流式处理来高效处理大型 JSON 文件。
-
如果在
jsonKeysToUse中指定了多个键,内容将是这些键值的连接。 -
通过自定义
jsonKeysToUse和JsonMetadataGenerator,读取器可以适应各种 JSON 结构。
文本
TextReader处理纯文本文档,将它们转换为Document对象列表。
示例
@Component
class MyTextReader {
private final Resource resource;
MyTextReader(@Value("classpath:text-source.txt") Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
List<Document> loadText() {
TextReader textReader = new TextReader(this.resource);
textReader.getCustomMetadata().put("filename", "text-source.txt");
return textReader.read();
}
}
构造函数选项
TextReader提供了两个构造函数选项:
-
TextReader(String resourceUrl) -
TextReader(Resource resource)
参数
-
resourceUrl: 表示要读取的资源 URL 的字符串。 -
resource: 指向文本文件的 SpringResource对象。
配置
-
setCharset(Charset charset): 设置用于读取文本文件的字符集。默认为 UTF-8。 -
getCustomMetadata(): 返回一个可变映射,您可以��在其中添加文档的自定义元数据。
行为
TextReader按以下方式处理文本内容:
-
它将文本文件的整个内容读入单个
Document对象。 -
文件的内容成为
Document的内容。 -
元数据自动添加到
Document:-
charset: 用于读取文件的字符集(默认:"UTF-8")。 -
source: 源文本文件的文件名。
-
-
通过
getCustomMetadata()添加的任何自定义元数据都包含在Document中。
注意事项
-
TextReader将整个文件内容读入内存,因此可能不适合非常大的文件。 -
如果您需要将文本分割成更小的块,可以在读取文档后使用文本分割器,如
TokenTextSplitter:
List<Document> documents = textReader.get();
List<Document> splitDocuments = new TokenTextSplitter().apply(this.documents);
-
读取器使用 Spring 的
Resource抽象,允许从各种源(类路径、文件系统、URL 等)读取。 -
可以使用
getCustomMetadata()方法向读取器创建的所有文档添加自定义元数据。
HTML (JSoup)
JsoupDocumentReader使用 JSoup 库处理 HTML 文档,将它们转换为Document对象列表。
示例
@Component
class MyHtmlReader {
private final Resource resource;
MyHtmlReader(@Value("classpath:/my-page.html") Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
List<Document> loadHtml() {
JsoupDocumentReaderConfig config = JsoupDocumentReaderConfig.builder()
.selector("article p") // 提取<article>标签内的段落
.charset("ISO-8859-1") // 使用 ISO-8859-1 编码
.includeLinkUrls(true) // 在元数据中包含链接 URL
.metadataTags(List.of("author", "date")) // 提取作者和日期元标签
.additionalMetadata("source", "my-page.html") // 添加自定义元数据
.build();
JsoupDocumentReader reader = new JsoupDocumentReader(this.resource, config);
return reader.get();
}
}
-
JsoupDocumentReaderConfig允许您自定义JsoupDocumentReader的行为: -
charset: 指定 HTML 文档的字符编码(默认为"UTF-8")。 -
selector: 一个 JSoup CSS 选择器,用于指定要提取文本的元素(默认为"body")。 -
separator: 用于连接多个选定元素的文本的字符串(默认为"\n")。 -
allElements: 如果为true,则提取<body>元素中的所有文本,忽略selector(默认为false)。 -
groupByElement: 如果为true,则为selector匹配的每个元素创建单独的Document(默认为false)。 -
includeLinkUrls: 如果为true,则提取绝对链接 URL 并将它们添加到元数据中(默认为false)。 -
metadataTags: 要从中提取内容的<meta>标签名称列表(默认为["description", "keywords"])。 -
additionalMetadata: 允许您向所有创建的Document对象添加自定义元数据。
示例文档:my-page.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>My Web Page</title>
<meta name="description" content="A sample web page for Spring AI">
<meta name="keywords" content="spring, ai, html, example">
<meta name="author" content="John Doe">
<meta name="date" content="2024-01-15">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>Welcome to My Page</h1>
</header>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="/">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="/about">About</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<article>
<h2>Main Content</h2>
<p>This is the main content of my web page.</p>
<p>It contains multiple paragraphs.</p>
<a href="https://www.example.com">External Link</a>
</article>
<footer>
<p>© 2024 John Doe</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>
行为:
JsoupDocumentReader处理 HTML 内容并根据配置创建Document对象:
-
selector确定用于文本提取的元素。 -
如果
allElements为true,则从<body>中提取所有文本到单个Document中。 -
如果
groupByElement为true,则为selector匹配的每个元素创建单独的Document。 -
如果
allElements和groupByElement都不为true,则使用separator连接selector匹配的所有元素的文本。 -
文档标题、指定
<meta>标签的内容以及(可选)链接 URL 被添加到Document元数据中。 -
基本 URI(用于解析相对链接)将从 URL 资源中提取。
读取器保留选定元素的文本内容,但删除其中的任何 HTML 标签。
Markdown
MarkdownDocumentReader处理 Markdown 文档,将它们转换为Document对象列表。
示例
@Component
class MyMarkdownReader {
private final Resource resource;
MyMarkdownReader(@Value("classpath:code.md") Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
List<Document> loadMarkdown() {
MarkdownDocumentReaderConfig config = MarkdownDocumentReaderConfig.builder()
.withHorizontalRuleCreateDocument(true)
.withIncludeCodeBlock(false)
.withIncludeBlockquote(false)
.withAdditionalMetadata("filename", "code.md")
.build();
MarkdownDocumentReader reader = new MarkdownDocumentReader(this.resource, config);
return reader.get();
}
}
MarkdownDocumentReaderConfig允许您自定义 MarkdownDocumentReader 的行为:
-
horizontalRuleCreateDocument: 当设置为true时,Markdown 中的水平规则将创建新的Document对象。 -
includeCodeBlock: 当设置为true时,代码块将包含在与周围文本相同的Document中。当为false时,代码块创建单独的Document对象。 -
includeBlockquote: 当设置为true时,引用块将包含在与周围文本相同的Document中。当为false时,引用块创建单独的Document对象。 -
additionalMetadata: 允许您向所有创建的Document对象添加自定义元数据。
示例文档:code.md
This is a Java sample application:
```java
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
```
Markdown also provides the possibility to `use inline code formatting throughout` the entire sentence.
---
Another possibility is to set block code without specific highlighting:
```
./mvnw spring-javaformat:apply
```
行为:MarkdownDocumentReader 处理 Markdown 内容并根据配置创建 Document 对象:
-
标题成为 Document 对象中的元数据。
-
段落成为 Document 对象的内容。
-
代码块可以分离到它们自己的 Document 对象中,或包含在周围文本中。
-
引用块可以分离到它们自己的 Document 对象中,或包含在周围文本中。
-
水平规则可用于将内容分割成单独的 Document 对象。
读取器在 Document 对象的内容中保留格式,如内联代码�、列表和文本样式。
PDF 页面
PagePdfDocumentReader使用 Apache PdfBox 库解析 PDF 文档
使用 Maven 或 Gradle 将依赖项添加到您的项目中。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-pdf-document-reader</artifactId>
</dependency>
或添加到您的 Gradle build.gradle构建文件中。
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.ai:spring-ai-pdf-document-reader'
}
示例
@Component
public class MyPagePdfDocumentReader {
List<Document> getDocsFromPdf() {
PagePdfDocumentReader pdfReader = new PagePdfDocumentReader("classpath:/sample1.pdf",
PdfDocumentReaderConfig.builder()
.withPageTopMargin(0)
.withPageExtractedTextFormatter(ExtractedTextFormatter.builder()
.withNumberOfTopTextLinesToDelete(0)
.build())
.withPagesPerDocument(1)
.build());
return pdfReader.read();
}
}
PDF 段落
ParagraphPdfDocumentReader使用 PDF 目录(例如 TOC)信息将输入 PDF 分割成文本段落,并为每个段落输出一个`Document。 注意:并非所有 PDF 文档都包含 PDF 目录。
依赖项
使用 Maven 或 Gradle 将依赖项添加到您的项目中。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-pdf-document-reader</artifactId>
</dependency>
或添加到您的 Gradle build.gradle构建文件中。
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.ai:spring-ai-pdf-document-reader'
}
示例
@Component
public class MyPagePdfDocumentReader {
List<Document> getDocsFromPdfWithCatalog() {
ParagraphPdfDocumentReader pdfReader = new ParagraphPdfDocumentReader("classpath:/sample1.pdf",
PdfDocumentReaderConfig.builder()
.withPageTopMargin(0)
.withPageExtractedTextFormatter(ExtractedTextFormatter.builder()
.withNumberOfTopTextLinesToDelete(0)
.build())
.withPagesPerDocument(1)
.build());
return pdfReader.read();
}
}
Tika (DOCX, PPTX, HTML…)
TikaDocumentReader使用 Apache Tika 从各种文档格式中提取文本,如 PDF、DOC/DOCX、PPT/PPTX 和 HTML。有关支持的格式的完整列表,请参阅 https://tika.apache.org/3.1.0/formats.html[Tika 文档]。
依赖项
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-tika-document-reader</artifactId>
</dependency>
或添加到您的 Gradle build.gradle构建文件中�。
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.ai:spring-ai-tika-document-reader'
}
示例
@Component
class MyTikaDocumentReader {
private final Resource resource;
MyTikaDocumentReader(@Value("classpath:/word-sample.docx")
Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
List<Document> loadText() {
TikaDocumentReader tikaDocumentReader = new TikaDocumentReader(this.resource);
return tikaDocumentReader.read();
}
}
转换器
TextSplitter
TextSplitter是一个抽象基类,帮助将文档分割以适应 AI 模型的上下文窗口。
TokenTextSplitter
TokenTextSplitter是TextSplitter的实现,它使用 CL100K_BASE 编码基于标记计数将文本分割成块。
用法
@Component
class MyTokenTextSplitter {
public List<Document> splitDocuments(List<Document> documents) {
TokenTextSplitter splitter = new TokenTextSplitter();
return splitter.apply(documents);
}
public List<Document> splitCustomized(List<Document> documents) {
TokenTextSplitter splitter = new TokenTextSplitter(1000, 400, 10, 5000, true);
return splitter.apply(documents);
}
}
构造函数选项
TokenTextSplitter提供了两个构造函数选项:
-
TokenTextSplitter(): 创建具有默认设置的分割器。 -
TokenTextSplitter(int defaultChunkSize, int minChunkSizeChars, int minChunkLengthToEmbed, int maxNumChunks, boolean keepSeparator)
参数
-
defaultChunkSize: 每个文本块的目标大小(以标记为单位)(默认:800)。 -
minChunkSizeChars: 每个文本块的最小大小(以字符为单位)(默认:350)。 -
minChunkLengthToEmbed: 要包含的块的最小长度(默认:5)。 -
maxNumChunks: 从文本生成的最大块数(默认:10000)。 -
keepSeparator: 是否在块中保留分隔符(如换行符)(默认:true)。
行为
TokenTextSplitter按以下方式处理文本内容:
-
它使��用 CL100K_BASE 编码将输入文本编码为标记。
-
它根据
defaultChunkSize将编码文本分割成块。 -
对于每个块:
-
它将块解码回文本。
-
它尝试在
minChunkSizeChars之后找到合适的分断点(句号、问号、感叹号或换行符)。 -
如果找到分断点,它在该点截断块。
-
它修剪块并根据
keepSeparator设置可选地删除换行符。 -
如果结果块长于
minChunkLengthToEmbed,则将其添加到输出中。
-
-
此过程继续,直到处理完所有标记或达到
maxNumChunks。 -
如果剩余文本长于
minChunkLengthToEmbed,则将其作为最终块添加。
示例
Document doc1 = new Document("This is a long piece of text that needs to be split into smaller chunks for processing.",
Map.of("source", "example.txt"));
Document doc2 = new Document("Another document with content that will be split based on token count.",
Map.of("source", "example2.txt"));
TokenTextSplitter splitter = new TokenTextSplitter();
List<Document> splitDocuments = this.splitter.apply(List.of(this.doc1, this.doc2));
for (Document doc : splitDocuments) {
System.out.println("Chunk: " + doc.getContent());
System.out.println("Metadata: " + doc.getMetadata());
}
注意事项
-
TokenTextSplitter使用来自jtokkit库的 CL100K_BASE 编码,它与较新的 OpenAI 模型兼容。 -
分割器尝试通过在可能的情况下在句子边界处断开来创建语义上有意义的块。
-
原始文档的元数据被保留并复制到从该文档派生的所有块中。
-
如果
copyContentFormatter设置为true(默认行为),原始文档的内容格式化程序(如果设置)也会复制到派生的块中。 -
此分割器特别适用于为具有标记限制的大型语言模型准备文本,确保每个块都在模型的处理能力范围内。
ContentFormatTransformer
确保所有文档的内容格式统一。
KeywordMetadataEnricher
KeywordMetadataEnricher是一个DocumentTransformer,它使用生成式 AI 模型从文档内容中提取关键词并将它们添加为元数据。
用法
@Component
class MyKeywordEnricher {
private final ChatModel chatModel;
MyKeywordEnricher(ChatModel chatModel) {
this.chatModel = chatModel;
}
List<Document> enrichDocuments(List<Document> documents) {
KeywordMetadataEnricher enricher = new KeywordMetadataEnricher(this.chatModel, 5);
return enricher.apply(documents);
}
}
构造函数
KeywordMetadataEnricher构造函数接受两个参数:
-
ChatModel chatModel: 用于生成关键词的 AI 模型。 -
int keywordCount: 为每个文档提取的关键词数量。
行为
KeywordMetadataEnricher按以下方式处理文档:
-
对于每个输入文档,它使用文档的内容创建提示。
-
它将此提示发送到提供的
ChatModel以生成关键词。 -
生成的关键词被添加到文档的�元数据中,键为"excerpt_keywords"。
-
返回富集后的文档。
自定义
可以通过修改类中的KEYWORDS_TEMPLATE常量来自定义关键词提取提示。默认模板是:
\{context_str}. Give %s unique keywords for this document. Format as comma separated. Keywords:
其中{context_str}被替换为文档内容,%s被替换为指定的关键词数量。
示例
ChatModel chatModel = // 初始化您的聊天模型
KeywordMetadataEnricher enricher = new KeywordMetadataEnricher(chatModel, 5);
Document doc = new Document("This is a document about artificial intelligence and its applications in modern technology.");
List<Document> enrichedDocs = enricher.apply(List.of(this.doc));
Document enrichedDoc = this.enrichedDocs.get(0);
String keywords = (String) this.enrichedDoc.getMetadata().get("excerpt_keywords");
System.out.println("Extracted keywords: " + keywords);
注意事项
-
KeywordMetadataEnricher需要一个正常工作的ChatModel来生成关键词。 -
关键词数量必须为 1 或更大。
-
富集器向每个处理的文档添加"excerpt_keywords"元数据字段。
-
生成的关键词作为逗号分隔的字符串返回。
-
此富集器特别适用于提高文档的可搜索性以及为文档生成标签或类别。
SummaryMetadataEnricher
SummaryMetadataEnricher是一个DocumentTransformer,它使用生成式 AI 模型为文档创建摘要并将它们添加为元数据。它可以为当前文档以及相邻文档(前一个和后一个)生成摘要。
用法
@Configuration
class EnricherConfig {
@Bean
public SummaryMetadataEnricher summaryMetadata(OpenAiChatModel aiClient) {
return new SummaryMetadataEnricher(aiClient,
List.of(SummaryType.PREVIOUS, SummaryType.CURRENT, SummaryType.NEXT));
}
}
@Component
class MySummaryEnricher {
private final SummaryMetadataEnricher enricher;
MySummaryEnricher(SummaryMetadataEnricher enricher) {
this.enricher = enricher;
}
List<Document> enrichDocuments(List<Document> documents) {
return this.enricher.apply(documents);
}
}
构造函数
SummaryMetadataEnricher提供了两个构造函数:
-
SummaryMetadataEnricher(ChatModel chatModel, List<SummaryType> summaryTypes) -
SummaryMetadataEnricher(ChatModel chatModel, List<SummaryType> summaryTypes, String summaryTemplate, MetadataMode metadataMode)
参数
-
chatModel: 用于生成摘要的 AI 模型。 -
summaryTypes: 指示要生��成哪些摘要的SummaryType枚举值列表(PREVIOUS, CURRENT, NEXT)。 -
summaryTemplate: 用于摘要生成的自定义模板(可选)。 -
metadataMode: 指定在生成摘要时如何处理文档元数据(可选)。
行为
SummaryMetadataEnricher按以下方式处理文档:
-
对于每个输入文档,它使用文档内容和指定的摘要模板创建提示。
-
它将此提示发送到提供的
ChatModel以生成摘要。 -
根据指定的
summaryTypes,它向每个文档添加以下元数据:-
section_summary: 当前文档的摘要。 -
prev_section_summary: 前一个文档的摘要(如果可用且请求)。 -
next_section_summary: 下一个文档的摘要(如果可用且请求)。
-
-
返回富集后的文档。
自定义
可以通过提供自定义summaryTemplate来自定义摘要生成提示。默认模板是:
"""
Here is the content of the section:
{context_str}
Summarize the key topics and entities of the section.
Summary:
"""
示例
ChatModel chatModel = // 初始化您的聊天模型
SummaryMetadataEnricher enricher = new SummaryMetadataEnricher(chatModel,
List.of(SummaryType.PREVIOUS, SummaryType.CURRENT, SummaryType.NEXT));
Document doc1 = new Document("Content of document 1");
Document doc2 = new Document("Content of document 2");
List<Document> enrichedDocs = enricher.apply(List.of(this.doc1, this.doc2));
// 检查富集后文档的元数据
for (Document doc : enrichedDocs) {
System.out.println("Current summary: " + doc.getMetadata().get("section_summary"));
System.out.println("Previous summary: " + doc.getMetadata().get("prev_section_summary"));
System.out.println("Next summary: " + doc.getMetadata().get("next_section_summary"));
}
提供的示例演示了预期行为:
-
对于两个文档的列表,两个文档都接收
section_summary。 -
第一个文档接收
next_section_summary但没有prev_section_summary。 -
第二个文档接收
prev_section_summary但没有next_section_summary。 -
第一个文档的
section_summary与第二个文档的prev_section_summary匹配。 -
第一个文档的
next_section_summary与第二个文档的section_summary匹配。
注意事项
-
SummaryMetadataEnricher需要一个正常工作的ChatModel来生成摘要。 -
富集器可以处理任何大小的文档列表,正确处理第一个和最后一个文档的边缘情况。
-
此富集器特别适用于创建上下文感知的摘要,允许更好地理解序列中文档的关系。
-
MetadataMode参数允许控制如何在摘要生成过程中合并现有元数据。
写入器
文件
FileDocumentWriter是一个DocumentWriter实现,它将Document对象列表的内容写入文件。
用法
@Component
class MyDocumentWriter {
public void writeDocuments(List<Document> documents) {
FileDocumentWriter writer = new FileDocumentWriter("output.txt", true, MetadataMode.ALL, false);
writer.accept(documents);
}
}
构造函数
FileDocumentWriter提供了三个构造函数:
-
FileDocumentWriter(String fileName) -
FileDocumentWriter(String fileName, boolean withDocumentMarkers) -
FileDocumentWriter(String fileName, boolean withDocumentMarkers, MetadataMode metadataMode, boolean append)
参数
-
fileName: 要写入文档的文件名。 -
withDocumentMarkers: 是否在输出中包含文档标记(默认:false)。 -
metadataMode: 指定要写入文件的文档内容(默认:MetadataMode.NONE)。 -
append: 如果为 true,数据将写入文件末尾而不是开头(默认:false)。
行为
FileDocumentWriter按以下方式处理文档:
-
它为指定的文件名打开一个 FileWriter。
-
对于输入列表中的每个文档:
-
如果
withDocumentMarkers为 true,它写入包含文档索引和页码的文档标记。 -
它根据指定的
metadataMode写入文档的格式化内容。
-
-
写入所有文档后关闭文件。
文档标记
当withDocumentMarkers设置为 true 时,写入器为每个文档包含以下格式的标记:
### Doc: [index], pages:[start_page_number,end_page_number]
元数据处理
写入器使用两个特定的元数据键:
-
page_number: 表示文档的起始页码。 -
end_page_number: 表示文档的结束页码。
这些在写入文档标记时使用。
示例
List<Document> documents = // 初始化您的文档
FileDocumentWriter writer = new FileDocumentWriter("output.txt", true, MetadataMode.ALL, true);
writer.accept(documents);
这将把所有文档写入"output.txt",包括文档标记,使用所有可用的元数据,如果文件已存在则追加到文件。
注意事项
-
写入器使用
FileWriter,因此它使用操作系统的默认字符编码写入文本文件。 -
如果在写入过程中发生错误,将抛出带有原始异常作为原因的
RuntimeException。 -
metadataMode参数允许控制如何将现有元数据合并到写入的内容中。 -
此写入器特别适用于调试或创建文档集合的人类可读输出。
VectorStore
提供与各种向量存储的集成。