多智能体(Multi-agent)
Multi-agent 将复杂的应用程序分解为多个协同工作的专业化Agent。与依赖单个Agent处理所有步骤不同,Multi-agent架构允许你将更小、更专注的Agent组合成协调的工作流。
Multi-agent系统在以下情况下很有用:
- 单个Agent拥有太多工具,难以做出正确的工具选择决策
- 上下文或记忆增长过大,单个Agent难以有效跟踪
- 任务需要专业化(例如:规划器、研究员、数学专家)
Multi-agent模式
Spring AI Alibaba支持以下Multi-agent模式:
| 模式 | 工作原理 | 控制流 | 使用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tool Calling | Supervisor Agent将其他Agent作为工具调用。"工具"Agent不直接与用户对话——它们只执行任务并返回结果。 | 集中式:所有路由都通过调用Agent。 | 任务编排、结构化工作流。 |
| Handoffs | 当前的Agent决定将控制权转移给另一个Agent。活动Agent随之变更,用户可以继续与新的Agent直接交互。 | 去中心化:Agent可以改变当前由谁来担当活跃Agent。 | 跨领域对话、专家接管。 |
选择模式
| 问题 | 工具调用 (Agent Tool) | 交接(Handoffs) |
|---|---|---|
| 需要集中控制工作流程? | ✅ 是 | ❌ 否 |
| 希望Agent直接与用户交互? | ❌ 否 | ✅ 是 |
| 专家之间复杂的、类人对话? | ❌ 有限 | ✅ 强 |
你可以混合使用两种模式——使用交接进行Agent切换,并让每个Agent将子Agent作为工具调用来执行专门任务。
关于工具调用模式的使用请查看 Agent Tool 文档。
自定义Agent上下文
Multi-agent设计的核心是上下文工程——决定每个Agent看到什么信息。Spring AI Alibaba 为你提供细粒度的控制:
- 将对话或状态的哪些部分传递给每个Agent
- 为子Agent定制专门的提示
- 包含/排除中间推理
- 为每个Agent自定义输入/输出格式
系统的质量在很大程度上取决于上下文工程。目标是确保每个Agent都能访问执行任务所需的正确数据,无论它是作为工具还是作为活动Agent。
Instruction 占位符
在 Multi-agent 系统中,instruction 支持使用占位符来动态引用状态中的数据。这是实现 Agent 之间数据传递的关键机制。
支持的占位符
| 占位符 | 说明 | 使用场景 |
|---|---|---|
{input} | 用户输入的原始内容 | 第一个Agent或需要用户输入的 Agent |
{outputKey} | 引用其他Agent通过 outputKey 存储的输出 | 顺序执行中,后续Agent引用前面Agent的输出 |
{stateKey} | 引用状态中的任意键值 | 访问状态中的任何数据 |
占位符工作原理
- 自动替换:系统会在执行 Agent 的 instruction 时,自动将占位符替换为对应的实际值
- 状态查找:占位符会从当前状态(
OverAllState)中查找对应的值 - 类型安全:占位符的值会被转换为字符串并插入到 instruction 中
使用示例
// 第一个Agent:使用 {input} 获取用户输入
ReactAgent writerAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("writer_agent")
.instruction("你是一个知名的作家。请根据用户的提问进行回答:{input}。")
.outputKey("article")
.build();
// 第二个Agent:使用 {article} 引用第一个Agent的输出
ReactAgent reviewerAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("reviewer_agent")
.instruction("请对文章进行评审修正:\n{article},最终返回评审修正后的文章内容")
.outputKey("reviewed_article")
.build();
最佳实践
- 明确命名:使用有意义的
outputKey,便于后续Agent引用 - 占位符格式:使用
{keyName}格式,确保与outputKey一致 - 错误处理:如果占位符对应的值不存在,系统会保留原始占位符文本
- 多值引用:可以在一个 instruction 中使用多个占位符
💡 提示:占位符机制使得 Agent 之间的数据传递变得简单直观,无需手动管理状态传递逻辑。
交接(Handoffs)
💡 重要参数说明:在多 Agent 模式下,以下参数对于控制 Agent 行为和上下文传递至关重要:
instruction:用于在当前 Agent 节点处插入新的问题说明,引导模型和流程运行。支持使用占位符(如{input}、{outputKey}等)来动态引用状态中的数据,实现 Agent 之间的数据传递。
returnReasoningContent:控制子 Agent 的上下文是否返回父流程中。如果设置为false,则其他 Agent 不会有机会看到这个子 Agent 内部的推理过程,它们只能看到这个 Agent 输出的内容(比如通过outputKey引用)。这对于减少上下文大小、提高效率非常有用。
includeContents:父流程中可能包含非常多子 Agent 的推理过程、每个子 Agent 的输出等。includeContents用来控制当前子 Agent 执行时,是只基于自己的instruction给到的内容工作,还是会带上所有父流程的上下文。设置为false可以让子 Agent 专注于自己的任务,不受父流程复杂上下文的影响。
outputKey:指定输出内容的键名,可被后续 Agent 通过占位符引用(如{outputKey})。使用有意义的outputKey名称,便于后续 Agent 引用和状态管理。
systemPrompt和instruction(Routing 和 Supervisor):LlmRoutingAgent和SupervisorAgent还支持定制systemPrompt和instruction,用于覆盖默认实现,控制后续任务流转的行为。systemPrompt定义路由决策的整体框架,instruction提供具体的路由指导。
在交接模式中,Agent可以直接将控制权传递给彼此。"活动"Agent会发生变化,用户与当前拥有控制权的Agent进行交互。
流程:
- 当前Agent决定它需要另一个Agent的帮助
- 它将控制权(和状态)传递给下一个Agent
- 新Agent直接与用户交互,直到它决定再次交接或完成
顺序执行(Sequential Agent)
在顺序执行模式中,多个Agent按预定义的顺序依次执行。每个Agent的输出成为下一个Agent的输入。
流程:
- Agent A处理初始输入
- Agent A的输出传递给Agent B
- Agent B处理并传递给Agent C
- 最后一个Agent返回最终结果

实现
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.flow.agent.SequentialAgent;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.OverAllState;
// 创建专业化的子Agent
ReactAgent writerAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("writer_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("专业写作Agent")
.instruction("你是一个知名的作家,擅长写作和创作。请根据用户的提问进行回答:{input}。")
.outputKey("article")
.build();
ReactAgent reviewerAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("reviewer_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("专业评审Agent")
.instruction("你是一个知名的评论家,擅长对文章进行评论和修改。" +
"对于散文类文章,请确保文章中必须包含对于西湖风景的描述。待评论文章:
{article}" +
"最终只返回修改后的文章,不要包含任何评论信息。")
.outputKey("reviewed_article")
.build();
// 创建顺序Agent
SequentialAgent blogAgent = SequentialAgent.builder()
.name("blog_agent")
.description("根据用户给定的主题写一篇文章,然后将文章交给评论员进行评论")
.subAgents(List.of(writerAgent, reviewerAgent))
.build();
// 使用
Optional<OverAllState> result = blogAgent.invoke("帮我写一个100字左右的散文");
if (result.isPresent()) {
OverAllState state = result.get();
// 访问第一个Agent的输出
state.value("article").ifPresent(article -> {
if (article instanceof AssistantMessage) {
System.out.println("原始文章: " + ((AssistantMessage) article).getText());
}
});
// 访问第二个Agent的输出
state.value("reviewed_article").ifPresent(reviewedArticle -> {
if (reviewedArticle instanceof AssistantMessage) {
System.out.println("评审后文章: " + ((AssistantMessage) reviewedArticle).getText());
}
});
}
关键特性
- 按顺序执行:Agent按照
subAgents列表中定义的顺序执行 - 状态传递:每个Agent的输出通过
outputKey存储在状态中,可被后续Agent访问 - 消息历史:默认情况下,所有Agent共享消息历史
- 推理内容控制:使用
returnReasoningContents控制是否在消息历史中包含中间推理
控制推理内容
ReactAgent writerAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("writer_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.returnReasoningContents(true)
.outputKey("article")
.build();
ReactAgent reviewerAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("reviewer_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.instruction("请对文章进行评审修正:
{article},最终返回评审修正后的文章内容")
.includeContents(true) // 包含上一个Agent的推理内容
.returnReasoningContents(true)
.outputKey("reviewed_article")
.build();
SequentialAgent blogAgent = SequentialAgent.builder()
.name("blog_agent")
.subAgents(List.of(writerAgent, reviewerAgent))
.build();
Optional<OverAllState> result = blogAgent.invoke("帮我写一个100字左右的散文");
if (result.isPresent()) {
// 消息历史将包含所有工具调用和推理过程
List<Message> messages = (List<Message>) result.get().value("messages").orElse(List.of());
System.out.println("消息数量: " + messages.size()); // 包含所有中间步骤
}
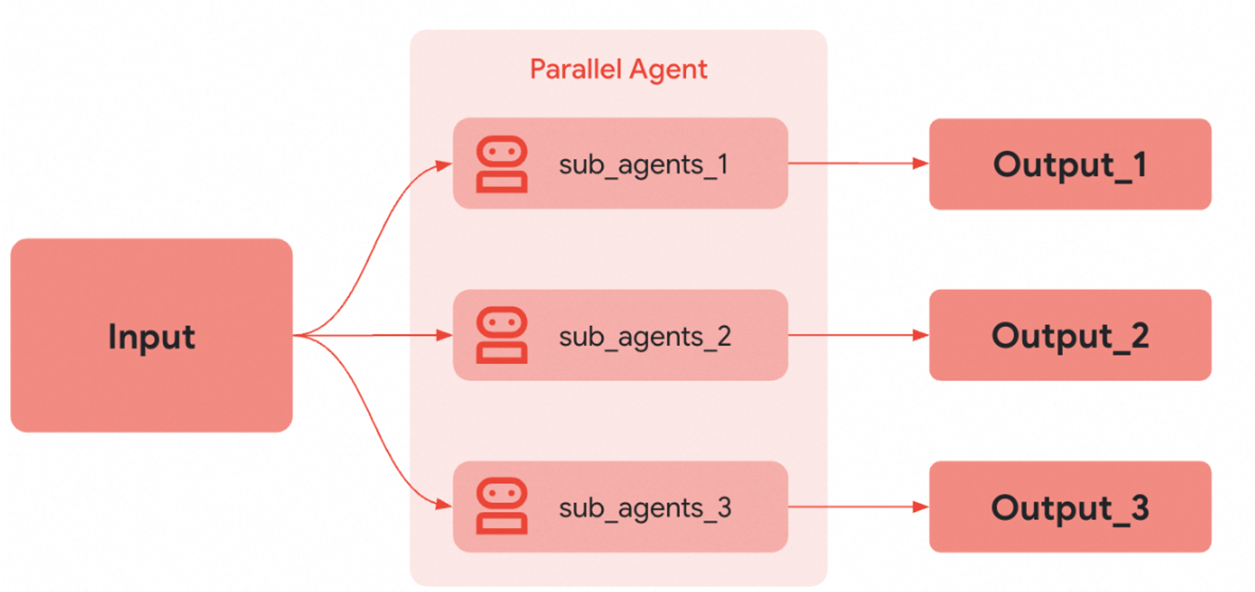
并行执行(Parallel Agent)
在并行执行模式中,多个Agent同时处理相同的输入。它们的结果被收集并合并。
流程:
- 输入同时发送给所有Agent
- 所有Agent并行处理
- 结果被合并成单一输出
实现
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.flow.agent.ParallelAgent;
// 创建多个专业化Agent
ReactAgent proseWriterAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("prose_writer_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("专门写散文的AI助手")
.instruction("你是一个知名的散文作家,擅长写优美的散文。" +
"用户会给你一个主题:{input},你只需要创作一篇100字左右的散文。")
.outputKey("prose_result")
.build();
ReactAgent poemWriterAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("poem_writer_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("专门写现代诗的AI助手")
.instruction("你是一个知名的现代诗人,擅长写现代诗。" +
"用户会给你的主题是:{input},你只需要创作一首现代诗。")
.outputKey("poem_result")
.build();
ReactAgent summaryAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("summary_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("专门做内容总结的AI助手")
.instruction("你是一个专业的内容分析师,擅长对主题进行总结和提炼。" +
"用户会给你一个主题:{input},你只需要对这个主题进行简要总结。")
.outputKey("summary_result")
.build();
// 创建并行Agent
ParallelAgent parallelAgent = ParallelAgent.builder()
.name("parallel_creative_agent")
.description("并行执行多个创作任务,包括写散文、写诗和做总结")
.mergeOutputKey("merged_results")
.subAgents(List.of(proseWriterAgent, poemWriterAgent, summaryAgent))
.mergeStrategy(new ParallelAgent.DefaultMergeStrategy())
.build();
// 使用
Optional<OverAllState> result = parallelAgent.invoke("以'西湖'为主题");
if (result.isPresent()) {
OverAllState state = result.get();
// 访问各个Agent的输出
state.value("prose_result").ifPresent(r ->
System.out.println("散文: " + r));
state.value("poem_result").ifPresent(r ->
System.out.println("诗歌: " + r));
state.value("summary_result").ifPresent(r ->
System.out.println("总结: " + r));
// 访问合并后的结果
state.value("merged_results").ifPresent(r ->
System.out.println("合并结果: " + r));
}
自定义合并策略
你可以实现自定义的合并策略来控制如何组合多个Agent的输出:
public class CustomMergeStrategy implements ParallelAgent.MergeStrategy {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> merge(Map<String, Object> mergedState, OverAllState state) {
// 从每个Agent的状态中提取输出
state.data().forEach((key, value) -> {
if (key.endsWith("_result")) {
Message message = (Message) value;
Object existing = mergedState.get("all_results");
if (existing == null) {
mergedState.put("all_results", message.getText());
}
else {
mergedState.put("all_results", existing + "
---
" + message.getText());
}
}
});
return mergedState;
}
}
// 使用自定义合��并策略
ParallelAgent parallelAgent = ParallelAgent.builder()
.name("parallel_agent")
.subAgents(List.of(agent1, agent2, agent3))
.mergeStrategy(new CustomMergeStrategy())
.mergeOutputKey("final_merged_result")
.build();
路由(LlmRoutingAgent)
在路由模式中,使用大语言模型(LLM)动态决定将请求路由到哪个子Agent。这种模式非常适合需要智能选择不同专家Agent的场景。
流程:
- 路由Agent接收用户输入
- LLM分析输入并决定最合适的子Agent
- 选中的子Agent处理请求
- 结果返回给用户

实现
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.flow.agent.LlmRoutingAgent;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.ReactAgent;
// 创建专业化的子Agent
ReactAgent writerAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("writer_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("擅长创作各类文章,包括散文、诗歌等文学作品")
.instruction("你是一个知名的作家,擅长写作和创作。请根据用户的提问进行回答。")
.outputKey("writer_output")
.build();
ReactAgent reviewerAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("reviewer_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("擅长对文章进行评论、修改和润色")
.instruction("你是一个知名的评论家,擅长对文章进行评论和修改。" +
"对于散文类文章,请确保文章中必须包含对于西湖风景的描述。")
.outputKey("reviewer_output")
.build();
ReactAgent translatorAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("translator_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("擅长将文章翻译成各种语言")
.instruction("你是一个专业的翻译家,能够准确地将文章翻译成目标语言。")
.outputKey("translator_output")
.build();
// 创建路由Agent
LlmRoutingAgent routingAgent = LlmRoutingAgent.builder()
.name("content_routing_agent")
.description("根据用户需求智能路由到合适的专家Agent")
.model(chatModel)
.subAgents(List.of(writerAgent, reviewerAgent, translatorAgent))
.build();
// 使用 - LLM会自动选择最合适的Agent
Optional<OverAllState> result1 = routingAgent.invoke("帮我写一篇关于春天的散文");
// LLM会路由到 writerAgent
Optional<OverAllState> result2 = routingAgent.invoke("请帮我修改这篇文章:春天来了,花开了。");
// LLM会路由到 reviewerAgent
Optional<OverAllState> result3 = routingAgent.invoke("请将以下内容翻译成英文:春暖花开");
// LLM会路由到 translatorAgent
关键特性
- 智能路由:LLM根据输入内容和子Agent的描述自动选择最合适的Agent
- 灵活扩展:可以轻松添加新的专家Agent,LLM会自动识别并路由
- 描述驱动:子Agent的
description非常重要,它告诉LLM何时应该�选择该Agent - 单次执行:每次请求只路由到一个Agent执行
优化路由准确性
为了提高路由的准确性,需要注意以下几点:
// 1. 提供清晰明确的Agent描述
ReactAgent codeAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("code_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("专门处理编程相关问题,包括代码编写、调试、重构和优化。" +
"擅长Java、Python、JavaScript等主流编程语言。")
.instruction("你是一个资深的软件工程师...")
.build();
// 2. 明确Agent的职责边界
ReactAgent businessAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("business_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("专门处理商业分析、市场研究和战略规划问题。" +
"不处理技术实现细节。")
.instruction("你是一个资深的商业分析师...")
.build();
// 3. 使用不同领域的Agent避免重叠
LlmRoutingAgent routingAgent = LlmRoutingAgent.builder()
.name("multi_domain_router")
.model(chatModel)
.subAgents(List.of(codeAgent, businessAgent, writerAgent))
.build();
自定义系统提示和指令
LlmRoutingAgent 支持通过 systemPrompt 和 instruction 来自定义路由决策行为,提供更精确的路由控制。
使用 SystemPrompt
systemPrompt 用于设置路由决策的系统提示,会替换默认的系统提示。你可以通过它提供详细的决策规则和上下文:
final String ROUTING_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
你是一个智能的内容路由Agent,负责根据用户需求将任务路由到最合适的专家Agent。
## 你的职责
1. 仔细分析用户输入的意图和需求
2. 根据任务特性,选择最合适的专家Agent
3. 确保路由决策准确、高效
## 可用的子Agent及其职责
### writer_agent
- **功能**: 擅长创作各类文章,包括散文、诗歌等文学作品
- **适用场景**:
* 用户需要创作新文章、散文、诗歌等原创内容
* 简单的写作任务
- **输出**: writer_output
### reviewer_agent
- **功能**: 擅长对文章进行评论、修改和润色
- **适用场景**:
* 用户需要修改、评审或优化现有文章
* 需要提高文章质量
- **输出**: reviewer_output
### translator_agent
- **功能**: 擅长将文章翻译成各种语言
- **适用场景**:
* 用户需要将内容翻译成其他语言
* 多语言转换需求
- **输出**: translator_output
## 决策规则
1. **写作任务**: 如果用户需要创作新内容,选择 writer_agent
2. **修改任务**: 如果用户需要修改或优化现有内容,选择 reviewer_agent
3. **翻译任务**: 如果用户需要翻译内容,选择 translator_agent
## 响应格式
只返回Agent名称(writer_agent、reviewer_agent、translator_agent),不要包含其他解释。
""";
LlmRoutingAgent routingAgent = LlmRoutingAgent.builder()
.name("content_routing_agent")
.description("根据用户需求智能路由到合适的专家Agent")
.model(chatModel)
.systemPrompt(ROUTING_SYSTEM_PROMPT)
.subAgents(List.of(writerAgent, reviewerAgent, translatorAgent))
.build();
使用 Instruction
instruction 用于设置路由决策的用户指令,会作为 UserMessage 添加到消息列表中。你可以通过它提供额外的上下文信息或特定的路由指导:
// 使用 instruction 提供额外的路由指导
final String ROUTING_INSTRUCTION = """
请根据用户的需求,选择最合适的Agent来处理任务。
特别注意:
- 如果用户明确提到"写"、"创作"、"生成"等词汇,优先选择 writer_agent
- 如果用户提到"修改"、"优化"、"评审"等词汇,选择 reviewer_agent
- 如果用户提到"翻译"、"转换语言"等词汇,选择 translator_agent
""";
LlmRoutingAgent routingAgent = LlmRoutingAgent.builder()
.name("content_routing_agent")
.description("根据用户需求智能路由到合适的专家Agent")
.model(chatModel)
.instruction(ROUTING_INSTRUCTION)
.subAgents(List.of(writerAgent, reviewerAgent, translatorAgent))
.build();
同时使用 SystemPrompt 和 Instruction
你可以同时使用 systemPrompt 和 instruction 来提供更完整的路由决策上下文:
final String ROUTING_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
你是一个智能的内容路由Agent,负责根据用户需求将任务路由到最合适的专家Agent。
## 可用的子Agent及其职责
### writer_agent
- **功能**: 擅长创作各类文章
- **输出**: writer_output
### reviewer_agent
- **功能**: 擅长对文章进行评论、修改和润色
- **输出**: reviewer_output
### translator_agent
- **功能**: 擅长将文章翻译成各种语言
- **输出**: translator_output
## 响应格式
只返回Agent名称,不要包含其他解释。
""";
final String ROUTING_INSTRUCTION = """
请仔细分析用户输入,根据以下规则选择最合适的Agent:
1. 创作新内容 -> writer_agent
2. 修改现有内容 -> reviewer_agent
3. 翻译内容 -> translator_agent
""";
LlmRoutingAgent routingAgent = LlmRoutingAgent.builder()
.name("content_routing_agent")
.description("根据用户需求智能路由到合适的专家Agent")
.model(chatModel)
.systemPrompt(ROUTING_SYSTEM_PROMPT)
.instruction(ROUTING_INSTRUCTION)
.subAgents(List.of(writerAgent, reviewerAgent, translatorAgent))
.build();
SystemPrompt 和 Instruction 的区别
| 特性 | SystemPrompt | Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| 作用位置 | 系统消息(SystemMessage) | 用户消息(UserMessage) |
| 用途 | 定义路由Agent的角色、职责和决策规则 | 提供具体的路由指导或额外上下文 |
| 优先级 | 更高,影响整体路由行为 | 作为补充信息 |
| 使用场景 | 需要详细定义路由规则和Agent职责时 | 需要提供特定场景的路由指导时 |
💡 提示:
- 使用
systemPrompt来定义路由Agent的整体行为和决策框架- 使用
instruction来提供特定场景的路由指导或额外上下文- 两者可以配合使用,提供更精确的路由控制
监督者(SupervisorAgent)
在监督者模式中,使用大语言模型(LLM)作为监督者,动态决定将任务路由到哪个子Agent,并支持多步骤循环路由。与 LlmRoutingAgent 不同,SupervisorAgent 支持子Agent执行完成后返回监督者,监督者可以根据执行结果继续路由到其他Agent或完成任务。
流程:
- 监督者Agent接收用户输入或前序Agent的输出
- LLM分析当前状态并决定最合适的子Agent
- 选中的子Agent处理任务
- 子Agent执行完成后返回监督者
- 监督者根据结果决定:
- 继续路由到另一个子Agent(多步骤任务)
- 返回
FINISH完成任务
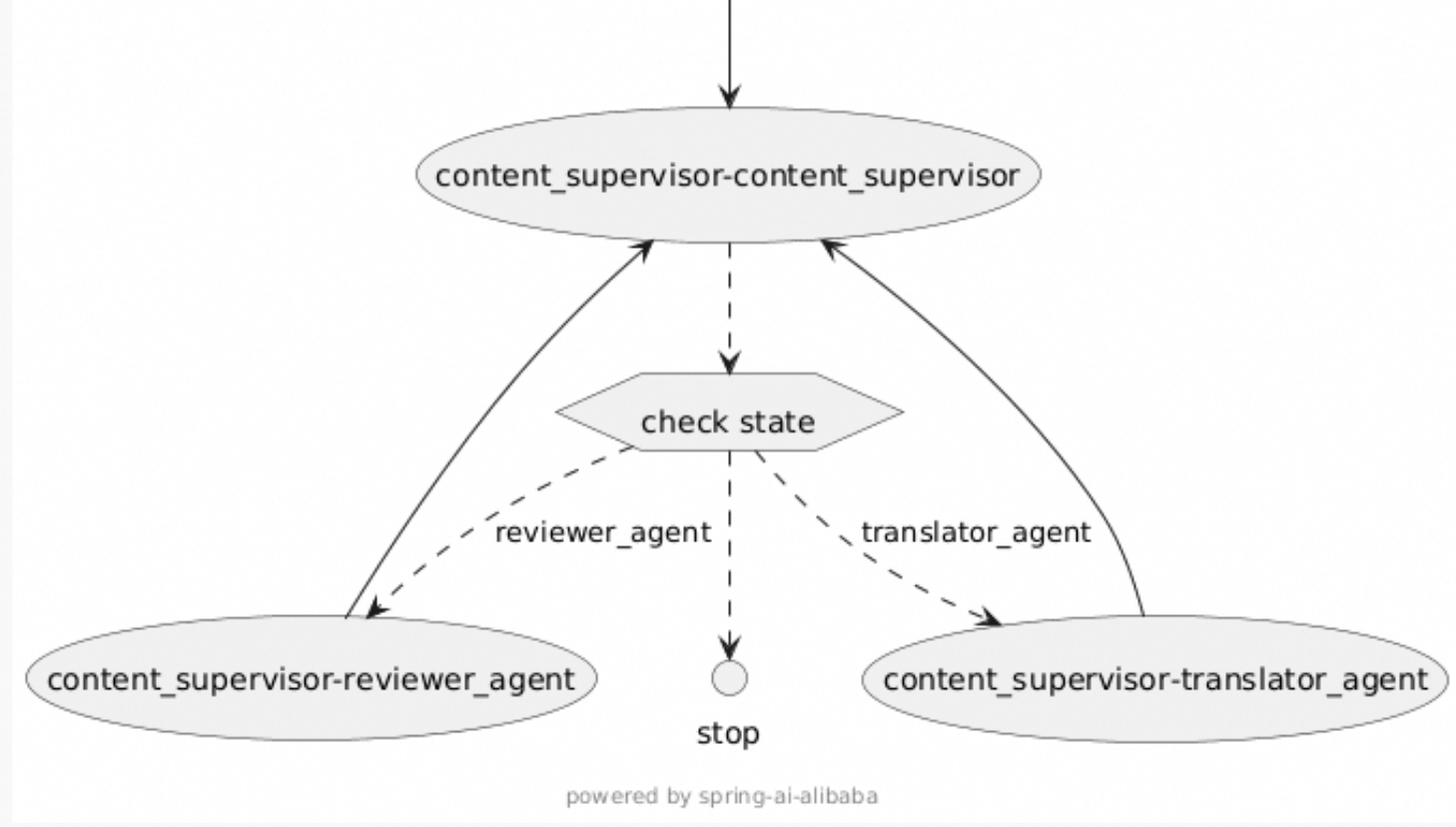
实现
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.flow.agent.SupervisorAgent;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.ReactAgent;
// 创建专业化的子Agent
ReactAgent writerAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("writer_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("擅长创作各类文章,包括散文、诗歌等文学作品")
.instruction("你是一个知名的作家,擅长写作和创作。请根据用户的提问进行回答。")
.outputKey("writer_output")
.build();
ReactAgent translatorAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("translator_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("擅长将文章翻译成各种语言")
.instruction("你是一个专业的翻译家,能够准确地将文章翻译成目标语言。")
.outputKey("translator_output")
.build();
// 创建监督者Agent
SupervisorAgent supervisorAgent = SupervisorAgent.builder()
.name("content_supervisor")
.description("内容管理监督者,负责协调写作、翻译等任务")
.model(chatModel)
.subAgents(List.of(writerAgent, translatorAgent))
.build();
// 使用 - 监督者会根据任务自动路由并支持多步骤处理
Optional<OverAllState> result = supervisorAgent.invoke("帮我写一篇关于春天的短文");
自定义系统提示
你可以通过 systemPrompt 为监督者提供详细的决策规则和上下文:
final String SUPERVISOR_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
你是一个智能的内容管理监督者,负责协调和管理多个专业Agent来完成用户的内容处理需求。
## 你的职责
1. 分析用户需求,将其分解为合适的子任务
2. 根据任务特性,选择合适的Agent进行处理
3. 监控任务执行状态,决定是否需要继续处理或完成任务
4. 当所有任务完成时,返回FINISH结束流程
## 可用的子Agent及其职责
### writer_agent
- **功能**: 擅长创作各类文章,包括散文、诗歌等文学作品
- **适用场景**:
* 用户需要创作新文章、散文、诗歌等原创内容
* 简单的写作任务,不需要后续评审或修改
- **输出**: writer_output
### translator_agent
- **功能**: 擅长将文章翻译成各种语言
- **适用场景**: 当文章需要翻译成其他语言时
- **输出**: translator_output
## 决策规则
1. **单一任务判断**:
- 如果用户只需要简单写作,选择 writer_agent
- 如果用户需要翻译,选择 translator_agent
2. **多步骤任务处理**:
- 如果用户需求包含多个步骤(如"先写文章,然后翻译"),需要分步处理
- 先路由到第一个合适的Agent,等待其完成
- 完成后,根据剩余需求继续路由到下一个Agent
- 直到所有步骤完成,返回FINISH
3. **任务完成判断**:
- 当用户的所有需求都已满足时,返回FINISH
## 响应格式
只返回Agent名称(writer_agent、translator_agent)或FINISH,不要包含其他解释。
""";
SupervisorAgent supervisorAgent = SupervisorAgent.builder()
.name("content_supervisor")
.description("内容管理监督者")
.model(chatModel)
.systemPrompt(SUPERVISOR_SYSTEM_PROMPT)
.subAgents(List.of(writerAgent, translatorAgent))
.build();
使用 Instruction 占位符
SupervisorAgent 支持通过 instruction 使用占位符来读取前序Agent的输出,这在 SupervisorAgent 作为 SequentialAgent 的子Agent时特别有用:
// 第一个Agent:写文章
ReactAgent articleWriterAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("article_writer")
.model(chatModel)
.description("专业写作Agent,负责创作文章")
.instruction("你是一个知名的作家,擅长写作和创作。请根据用户的提问进行回答:{input}。")
.outputKey("article_content")
.build();
// 监督者的子Agent
ReactAgent translatorAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("translator_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("擅长将文章翻译成各种语言")
.instruction("你是一个专业的翻译家,能够准确地将文章翻译成目标语言。待翻译文章:
{article_content}。")
.outputKey("translator_output")
.build();
ReactAgent reviewerAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("reviewer_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("擅长对文章进行评审和修改")
.instruction("你是一个知名的评论家,擅长对文章进行评论和修改。待评审文章:
{article_content}。")
.outputKey("reviewer_output")
.build();
// 监督者的instruction使用占位符读取前序Agent的输出
final String SUPERVISOR_INSTRUCTION = """
你是一个智能的内容处理监督者,你可以看到前序Agent的聊天历史与任务处理记录。当前,你收到了以下文章内容:
{article_content}
请根据文章内容的特点,决定是进行翻译还是评审:
- 如果文章是中文且需要翻译,选择 translator_agent
- 如果文章需要评审和改进,选择 reviewer_agent
- 如果任务完成,返回 FINISH
""";
final String SUPERVISOR_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
你是一个智能的内容处理监督者,负责协调翻译和评审任务。
## 可用的子Agent及其职责
### translator_agent
- **功能**: 擅长将文章翻译成各种语言
- **输出**: translator_output
### reviewer_agent
- **功能**: 擅长对文章进行评审和修改
- **输出**: reviewer_output
## 响应格式
只返回Agent名称(translator_agent、reviewer_agent)或FINISH,不要包含其他解释。
""";
// 创建SupervisorAgent,instruction中包含占位符
SupervisorAgent supervisorAgent = SupervisorAgent.builder()
.name("content_supervisor")
.description("内容处理监督者,根据前序Agent的输出决定翻译或评审")
.model(chatModel)
.systemPrompt(SUPERVISOR_SYSTEM_PROMPT)
.instruction(SUPERVISOR_INSTRUCTION)
.subAgents(List.of(translatorAgent, reviewerAgent))
.build();
// 创建SequentialAgent,SupervisorAgent作为子Agent
SequentialAgent sequentialAgent = SequentialAgent.builder()
.name("content_processing_workflow")
.description("内容处理工作流:先写文章,然后根据文章内容决定翻译或评审")
.subAgents(List.of(articleWriterAgent, supervisorAgent))
.build();
// 使用
Optional<OverAllState> result = sequentialAgent.invoke("帮我写一篇关于春天的短文,然后翻译成英文");
关键特性
- 多步骤循环路由:子Agent执行完成后会返回监督者,监督者可以继续路由到其他Agent,实现多步骤任务处理
- 智能决策:使用LLM分析当前状态和任务需求,动态选择最合适的子Agent
- Instruction占位符支持:
instruction支持使用占位符(如{article_content})读取前序Agent的输出 - 自定义系统提示:通过
systemPrompt提供详细的决策规则和上下文 - 自动重试机制:内置重试机制(最多2次),确保路由决策的可靠性
- 任务完成控制:监督者可以返回
FINISH来结束任务流程
与 LlmRoutingAgent 的区别
| 特性 | LlmRoutingAgent | SupervisorAgent |
|---|---|---|
| 路由次数 | 单次路由 | 支持多步骤循环路由 |
| 子Agent返回 | 直接结束 | 返回监督者继续决策 |
| 多步骤任务 | ❌ 不支持 | ✅ 支持 |
| Instruction占位符 | ❌ 不支持 | ✅ 支持 |
| 适用场景 | 简单的单次路由 | 复杂的多步骤任务编排 |
最佳实践
- 清晰的系统提示:提供详细的决策规则和子Agent职责描述,帮助LLM做出准确的路由决策
- 利用占位符:在
instruction中使用占位符读取前序Agent的输出,实现上下文感知的路由 - 明确的输出键:为每个子Agent设置有意义的
outputKey,便于后续Agent引用 - 任务分解:将复杂任务分解为多个步骤,让监督者逐步协调完成
- 嵌套使用:可以将
SupervisorAgent作为SequentialAgent的子Agent,实现更复杂的工作流
💡 提示:
SupervisorAgent特别适合需要多步骤任务编排的场景,例如"先写文章,然后翻译,最后评审"这样的复杂工作流。
自定义(Customized)
Spring AI Alibaba 提供了 FlowAgent 抽象类,允许你创建自定义的Agent工作流模式。通过继承 FlowAgent 并实现特定的图构建逻辑,你可以实现任何复杂的多Agent协作模式。
FlowAgent 架构
FlowAgent 是所有流程型Agent(如 SequentialAgent、ParallelAgent、LlmRoutingAgent)的基类,它提供了以下核心能力:
public abstract class FlowAgent extends Agent {
protected List<Agent> subAgents; // 子Agent列表
protected CompileConfig compileConfig; // 编译配置
// 核心抽象方法:子类必须实现具体的图构建逻辑
protected abstract StateGraph buildSpecificGraph(
FlowGraphBuilder.FlowGraphConfig config
) throws GraphStateException;
// 提供给子类使用的工具方法
public List<Agent> subAgents() { return this.subAgents; }
public CompileConfig compileConfig() { return compileConfig; }
}
实现自定义FlowAgent
下面展示如何创建一个自定义的 ConditionalAgent,它根据条件选择不同的Agent分支:
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.flow.agent.FlowAgent;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.flow.builder.FlowAgentBuilder;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.flow.builder.FlowGraphBuilder;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.StateGraph;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.CompileConfig;
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.Agent;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
/**
* 条件路由Agent:根据条件函数选择不同的Agent分支
*/
public class ConditionalAgent extends FlowAgent {
private final Predicate<Map<String, Object>> condition;
private final Agent trueAgent;
private final Agent falseAgent;
protected ConditionalAgent(ConditionalAgentBuilder builder) throws GraphStateException {
super(builder.name, builder.description, builder.compileConfig,
List.of(builder.trueAgent, builder.falseAgent));
this.condition = builder.condition;
this.trueAgent = builder.trueAgent;
this.falseAgent = builder.falseAgent;
}
@Override
protected StateGraph buildSpecificGraph(FlowGraphBuilder.FlowGraphConfig config)
throws GraphStateException {
// 使用 FlowGraphBuilder 构建自定义图结构
return FlowGraphBuilder.buildConditionalGraph(
config,
this.condition,
this.trueAgent,
this.falseAgent
);
}
public static ConditionalAgentBuilder builder() {
return new ConditionalAgentBuilder();
}
/**
* Builder for ConditionalAgent
*/
public static class ConditionalAgentBuilder
extends FlowAgentBuilder<ConditionalAgent, ConditionalAgentBuilder> {
private Predicate<Map<String, Object>> condition;
private Agent trueAgent;
private Agent falseAgent;
public ConditionalAgentBuilder condition(Predicate<Map<String, Object>> condition) {
this.condition = condition;
return this;
}
public ConditionalAgentBuilder trueAgent(Agent trueAgent) {
this.trueAgent = trueAgent;
return this;
}
public ConditionalAgentBuilder falseAgent(Agent falseAgent) {
this.falseAgent = falseAgent;
return this;
}
@Override
public ConditionalAgent build() throws GraphStateException {
if (condition == null || trueAgent == null || falseAgent == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Condition, trueAgent and falseAgent must be set");
}
return new ConditionalAgent(this);
}
@Override
protected ConditionalAgentBuilder self() {
return this;
}
}
}
使用自定义Agent
import com.alibaba.cloud.ai.graph.agent.ReactAgent;
import java.util.Map;
// 创建两个分支Agent
ReactAgent urgentAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("urgent_handler")
.model(chatModel)
.description("处理紧急请求")
.instruction("你需要快速响应紧急情况...")
.outputKey("urgent_result")
.build();
ReactAgent normalAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("normal_handler")
.model(chatModel)
.description("处理常规请求")
.instruction("你可以详细分析和处理常规请求...")
.outputKey("normal_result")
.build();
// 定义条件:检查输入是否包含"紧急"关键字
Predicate<Map<String, Object>> isUrgent = state -> {
Object input = state.get("input");
if (input instanceof String) {
return ((String) input).contains("紧急") || ((String) input).contains("urgent");
}
return false;
};
// 创建条件路由Agent
ConditionalAgent conditionalAgent = ConditionalAgent.builder()
.name("priority_router")
.description("根据紧急程度路由请求")
.condition(isUrgent)
.trueAgent(urgentAgent)
.falseAgent(normalAgent)
.build();
// 使用
Optional<OverAllState> result1 = conditionalAgent.invoke("这是一个紧急问题需要立即处理");
// 会路由到 urgentAgent
Optional<OverAllState> result2 = conditionalAgent.invoke("请帮我分析一下这个问题");
// 会路由到 normalAgent
实现复杂的循环Agent
你还可以创建更复杂的自定义Agent,例如带有循环逻辑的 LoopAgent:
/**
* 循环Agent:重复执行直到满足退出条件
*/
public class CustomLoopAgent extends FlowAgent {
private final Predicate<Map<String, Object>> exitCondition;
private final int maxIterations;
protected CustomLoopAgent(CustomLoopAgentBuilder builder)
throws GraphStateException {
super(builder.name, builder.description, builder.compileConfig, builder.subAgents);
this.exitCondition = builder.exitCondition;
this.maxIterations = builder.maxIterations;
}
@Override
protected StateGraph buildSpecificGraph(FlowGraphBuilder.FlowGraphConfig config)
throws GraphStateException {
// 构建带有循环逻辑的图
return FlowGraphBuilder.buildLoopGraph(
config,
this.exitCondition,
this.maxIterations
);
}
// Builder implementation...
}
// 使用示例
CustomLoopAgent refinementAgent = CustomLoopAgent.builder()
.name("iterative_refinement")
.subAgents(List.of(drafterAgent, reviewerAgent))
.exitCondition(state -> {
// 当质量分数 >= 8 时退出循环
Object score = state.get("quality_score");
return score != null && (int) score >= 8;
})
.maxIterations(5) // 最多循环5次
.build();
关键要点
扩展 FlowAgent 时需要注意:
- 实现 buildSpecificGraph:这是核心方法,定义了Agent的工作流逻辑
- 使用 FlowGraphBuilder:提供了构建图的工具方法
- 继承 FlowAgentBuilder:保持一致的构建器模式
- 管理子Agent:通过
subAgents列表管理所有子Agent - 状态传递:通过
StateGraph控制状态在Agent之间的流动
通过自定义 FlowAgent,你可以实现任意复杂的多Agent协作模式,满足各种业务场景需求。
混��合模式示例
你可以组合不同的模式创建复杂的工作流:
// 1. 创建研究Agent(并行执行)
ReactAgent webResearchAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("web_research")
.model(chatModel)
.description("从互联网搜索信息")
.instruction("请搜索并收集关于以下主题的信息:{input}")
.outputKey("web_data")
.build();
ReactAgent dbResearchAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("db_research")
.model(chatModel)
.description("从数据库查询信息")
.instruction("请从数据库中查询并收集关于以下主题的信息:{input}")
.outputKey("db_data")
.build();
ParallelAgent researchAgent = ParallelAgent.builder()
.name("parallel_research")
.description("并行收集多个数据源的信息")
.subAgents(List.of(webResearchAgent, dbResearchAgent))
.mergeOutputKey("research_data")
.build();
// 2. 创建分析Agent
ReactAgent analysisAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("analysis_agent")
.model(chatModel)
.description("分析研究数据")
.instruction("请分析以下收集到的数据并提供见解:{research_data}")
.outputKey("analysis_result")
.build();
// 3. 创建报告Agent(路由选择格式)
ReactAgent pdfReportAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("pdf_report")
.model(chatModel)
.description("生成PDF格式报告")
.instruction("""
请根据研究结果和分析结果生成一份PDF格式的报告。
研究结果:{research_data}
分析结果:{analysis_result}
""")
.outputKey("pdf_report")
.build();
ReactAgent htmlReportAgent = ReactAgent.builder()
.name("html_report")
.model(chatModel)
.description("生成HTML格式报告")
.instruction("""
请根据研究结果和分析结果生成一份HTML格式的报告。
研究结果:{research_data}
分析结果:{analysis_result}
""")
.outputKey("html_report")
.build();
LlmRoutingAgent reportAgent = LlmRoutingAgent.builder()
.name("report_router")
.description("根据需求选择报告格式")
.model(chatModel)
.subAgents(List.of(pdfReportAgent, htmlReportAgent))
.build();
// 4. 组合成顺序工作流
SequentialAgent hybridWorkflow = SequentialAgent.builder()
.name("research_workflow")
.description("完整的研究工作流:并行收集 -> 分析 -> 路由生成报告")
.subAgents(List.of(researchAgent, analysisAgent, reportAgent))
.build();
// 使用
Optional<OverAllState> result = hybridWorkflow.invoke("研究AI技术趋势并生成HTML报告");