Intelligent Flight Assistant
For the source code of this sample project, please refer to the Github repository spring-ai-alibaba-examples.
Next, we will demonstrate the powerful capabilities of Spring AI Alibaba in building agent applications through a more practical example.
The goal of this example is to use the Spring AI Alibaba framework to develop an intelligent flight assistant that can help consumers complete flight booking, answering questions, ticket rescheduling, cancellation, etc. The specific requirements are:
- Engage in conversation with users based on AI large models to understand users’ needs expressed in natural language
- Support multi-turn continuous conversation, able to understand user intent in context
- Understand and strictly follow terminology and regulations related to flight operations, such as aviation regulations, refund and rescheduling rules, etc.
- Call tools to assist in completing tasks when necessary
Complete Architecture Diagram
Based on the goal of an intelligent flight assistant, we have drawn the following architecture diagram:
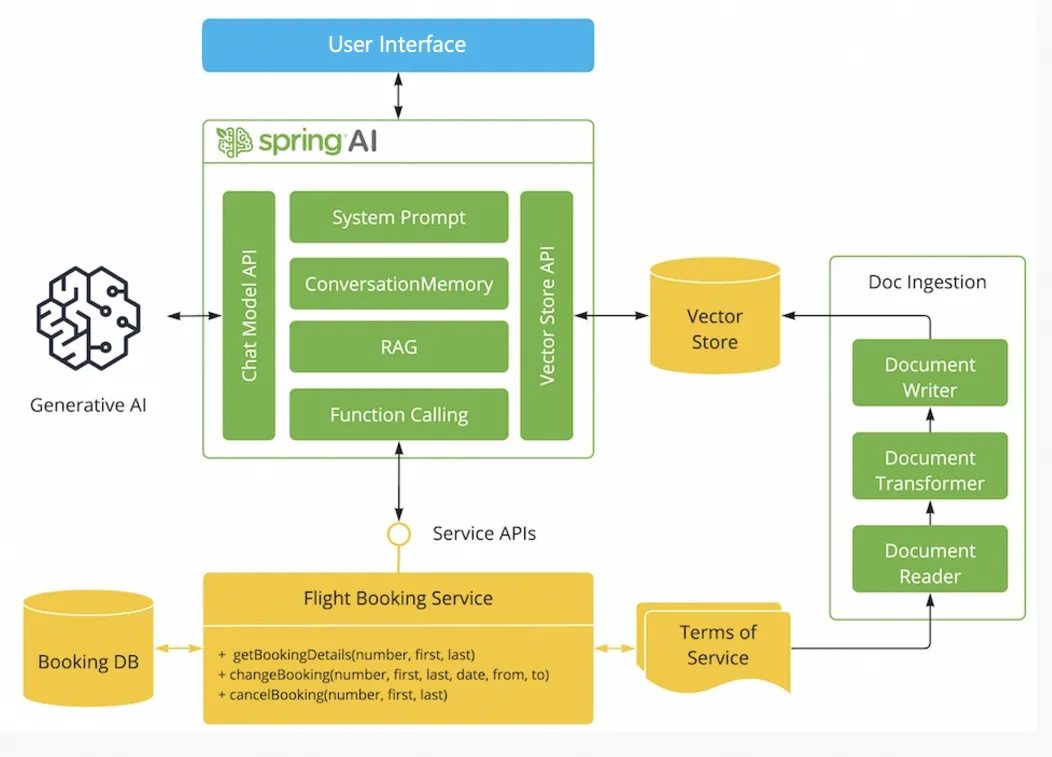
Next, we will analyze the example in detail in conjunction with the architecture diagram.
Integrating AI Model Services into the Application
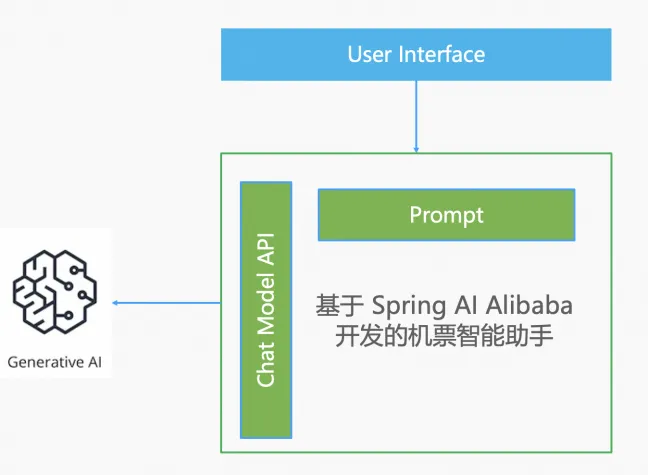
Essentially, we are developing a regular Java application with Spring Boot, which can continuously receive user questions and solve flight-related problems for users. It is called an agent application because it can interact with AI, allowing AI to help the application understand user problems and make decisions. Therefore, a simplified architecture diagram for our flight assistant is as follows:
Using RAG to Add Flight Refund and Rescheduling Rules
Based on the above architecture, the application uses the AI model to understand user questions, decide the next action, and drive business processes. But can any general large model help us solve flight-related problems? Is it reliable to rely on the model’s decisions? For example, if a user requests to reschedule a ticket, the model can certainly understand the user’s intent—there is no doubt about that. But how does it know whether the current user meets the refund rules? Each airline may have different rescheduling rules; how does it know the regulations for rescheduling fees? In such scenarios that may involve financial disputes or legal risks, the AI model must know all the details of the rescheduling rules and confirm that the user’s information meets the rules before making a final decision on whether to reschedule.
Obviously, relying solely on the AI model itself cannot meet the above requirements. This is where the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) pattern comes in. Through RAG, we can input domain knowledge related to flight refund and rescheduling into the application and AI model, allowing AI to assist in decision-making based on these rules and requirements. The architecture after adding RAG is as follows:
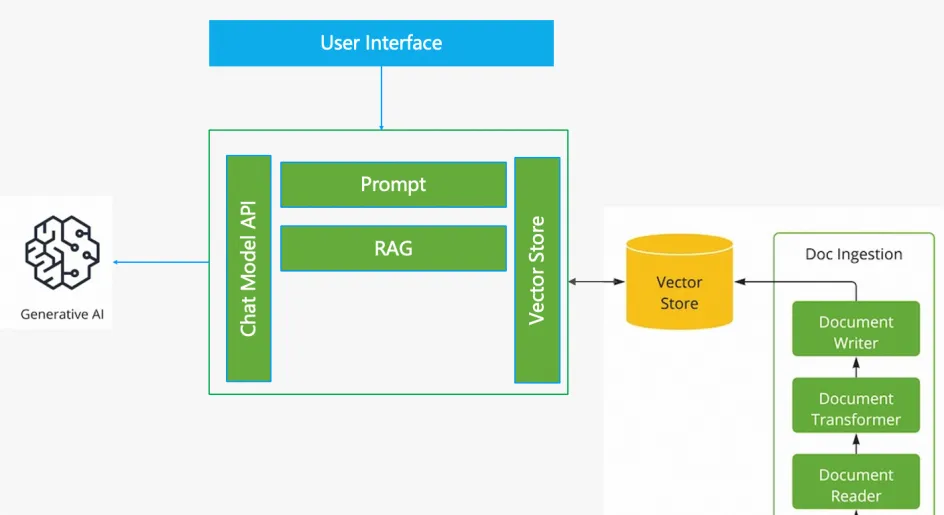
With RAG, our application truly becomes an intelligent flight expert, like a customer service representative trained in company business, able to converse humanely with users and guide user behavior according to the rules.
Using Function Calling to Execute Business Actions
The AI agent can help the application understand user needs and make decisions, but it cannot replace the application in executing those decisions. Execution must still be done by the application itself, just like in traditional applications. Whether intelligent or pre-orchestrated, the application must call functions to modify database records for data persistence.
With the Spring AI framework, we can convert model decisions into calls to specific functions, thereby completing the final rescheduling or refund actions for tickets and writing user data to the database. This is the Function Calling pattern mentioned earlier.

Using Chat Memory to Enable Multi-turn Conversation
The last point is about supporting multi-turn continuous conversation. Remember, large models are stateless—they only see the content of the current round of conversation. Therefore, to support multi-turn conversation, the application must retain the previous conversation context each time and send it along with the latest question as a prompt to the model. At this point, we can use the built-in Conversation Memory support provided by Spring AI Alibaba to conveniently maintain the conversation context.
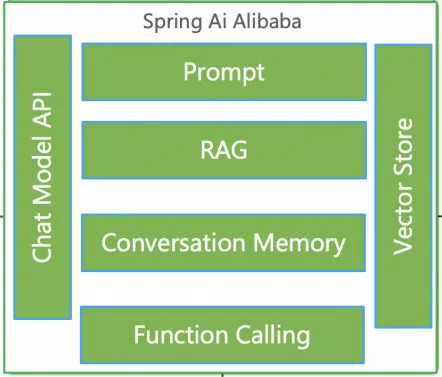
In summary, the core capabilities of Spring AI Alibaba used in this intelligent flight assistant application are:
- Basic model conversation capability, interacting with Alibaba Cloud Qwen model via Chat Model API
- Prompt management capability
- Chat Memory for multi-turn conversation support
- RAG, Vector Store for rules related to flight booking, rescheduling, refund, etc.
Coding with ChatClient
Spring AI Alibaba not only provides the above atomic capability abstractions but also offers a higher-level “Agent” API abstraction, ChatClient, allowing us to easily assemble multiple components into an agent using a fluent API. The usage of ChatClient is as follows:
this.chatClient = modelBuilder .defaultSystem(""" You are a customer chat support agent for "Funnair" Airlines. Please respond in a friendly, helpful, and pleasant manner. You are interacting with customers via an online chat system. Before providing information about booking or canceling a reservation, you must always obtain the following information from the user: booking number, customer name. Before asking the user, check the message history for this information. Before changing a reservation, you must ensure the terms allow it. If a change requires a fee, you must obtain the user's consent before proceeding. Use the provided functions to get booking details, change bookings, and cancel bookings. If necessary, call the corresponding function to complete auxiliary actions. Please speak Chinese. Today's date is {current_date}. """) .defaultAdvisors( new PromptChatMemoryAdvisor(chatMemory), // Chat Memory new VectorStoreChatMemoryAdvisor(vectorStore)), new QuestionAnswerAdvisor(vectorStore, SearchRequest.defaults()), // RAG new LoggingAdvisor()) .defaultFunctions("getBookingDetails", "changeBooking", "cancelBooking") // FUNCTION CALLING
.build();In this way,ChatClientshields us from all the details of interacting with large models. Simply inject ChatClientinto a regular Spring Bean to add intelligence to our flight application.
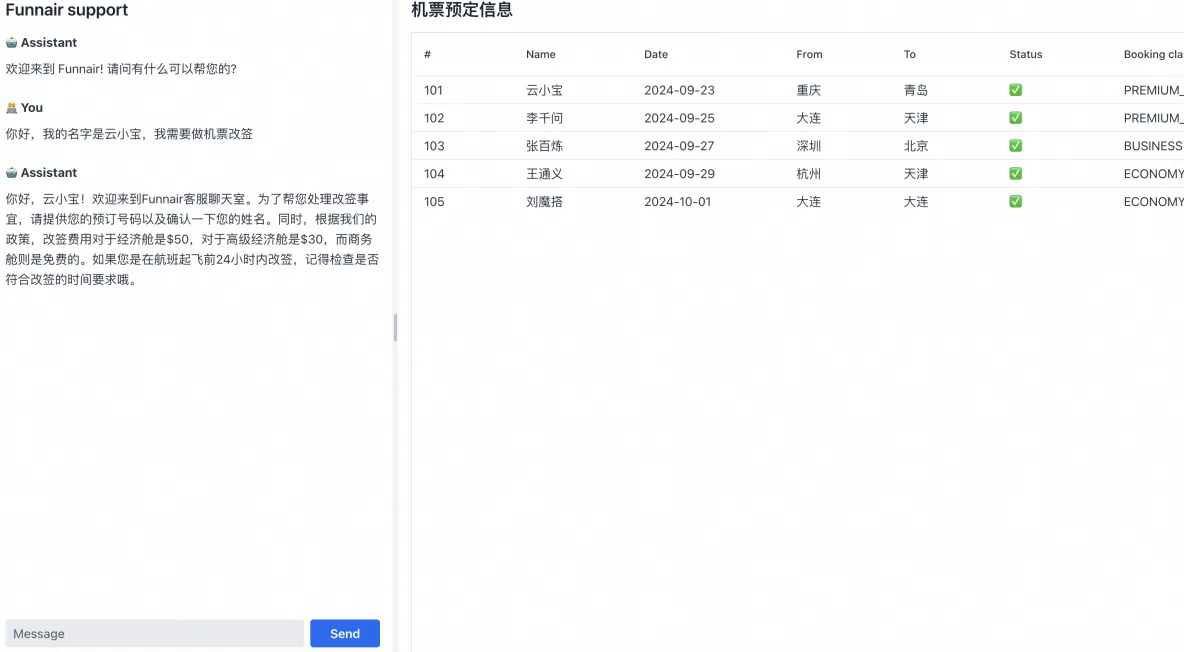
Finally, the running effect of our developed example is as follows: